Random Class in VB.NET
In this article I will explain you about generating Random Numbers Using random class in VB.NET.
Before we dive into the details of the System.Random class, we should talk about randomness in discrete mathematics. The two most common scenarios for generating random numbers are generating integers uniformly between 1 and n and generating real numbers uniformly between 0 and 1. Most random-number-generation algorithms are not influenced by the outside universe; they are inherently pseudorandom: predictable and following a pattern (ideally not an obvious one). You should keep in mind the following two statements on pseudorandomness made by respected computer science masters:
- "Anyone who considers arithmetical methods of producing random digits is, of course, in a state of sin." - John Von Neumann (1951)
- "Random number generators should not be chosen at random." - Donald Knuth (1986)
Let's go back to our main focus now. We use the System.Random class to produce a random number. System.Random can return both decimal and integer random numbers. In addition, System.Random by design can seed its random number generator with a random value derived from the computer system clock.
Dim rnd As New System.Random()
You can initialize the seed with any Int32 value on demand at times when the system clock is not fast enough to refresh or when you need to synchronize your random number generators across a network. This is also the common use of a seed to synchronize two random number generators.
Dim rnd As New System.Random(CInt(DateTime.Now.Ticks))
The Random class includes a series of methods allowing you to retrieve the next number produced by the random number generator. The NextDouble method returns a double random number between 0.0 and 1.0. The Next method returns an integer random number between two integer values. The NextBytes method fills the elements of a specified array of bytes with random numbers. The NextDouble, Next, and NextBytes methods are instance methods; therefore, you must instantiate a System.Random object before using them.
The Next() method has three overloads:
// a positive random number
Public Function [Next]() As Integer
End Function
// a positive random number less than the specified maximum
Public Function [Next](Integer) As Integer
End Function
// a random number within a specified range
Public Function [Next](Integer,Integer) As Integer
End Function
You can use the Next method overloads as shown in Listing 21.37.
Using the Next Property
// any valid integer random number
Dim dbl1 As Int32 = Rnd.[Next]()
// an integer between 0< and UpperBound where UpperBound + 1 >= 0
Dim dbl1 As Int32 = Rnd.[Next](UpperBound + 1)
// an integer between LowerBound< and UpperBound where UpperBound + 1 >= 0
// and LowerBound <= UpperBound + 1
Dim dbl1 As Int32 = Rnd.[Next](LowerBound, UpperBound + 1)
Using the NextDouble method of the Random class produces the next pseudorandom double value that is greater than 0.0 and less than 1.0.
Dim dbl1 As [Double] = Rnd.NextDouble()
The NextBytes method of the Random class produces an array of random bytes with values ranging from 0 to MaxValue (MaxValue = 255).
Dim mybytes As [Byte]() = New [Byte](4) {}
// mybytes is filled with 5 bytes of random data
rnd.NextBytes(mybytes)
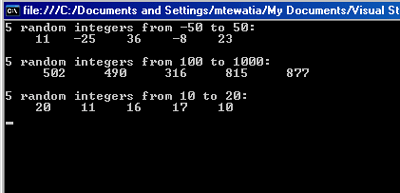
The program in Listing 21.38 generates unique integer random numbers in the ranges that you send to the application and then displays them on the console
Generating Unique Random Numbers with Next(Int32, Int32)
Module Example
Sub Main()
Dim rnd As New Random()
Console.WriteLine("5 random integers from -50 to 50:")
For ctr As Integer = 1 To 5
Console.Write("{0,6}", rnd.Next(-50, 51))
If ctr Mod 5 = 0 Then Console.WriteLine()
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Console.WriteLine("5 random integers from 100 to 1000:")
For ctr As Integer = 1 To 5
Console.Write("{0,8}", rnd.Next(100, 1001))
If ctr Mod 5 = 0 Then Console.WriteLine()
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Console.WriteLine("5 random integers from 10 to 20:")
For ctr As Integer = 1 To 5
Console.Write("{0,6}", rnd.Next(10, 21))
If ctr Mod 5 = 0 Then Console.WriteLine()
Next
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module
Output window
Conclusion
Hope this article would have helped you in understanding generating Random Numbers Using the Random Class in VB.NET.