Custom Exception Handling in VB.NET
This article gives you a idea about exception handling in Visual Basic.Net and also how you can create your own custom exceptions.
Exception
Exceptions are the occurrence of some condition that changes the normal flow of execution .
For example:
Your program run out of memory , file does not exist in the given path , network connections are dropped etc. More specifically for better understanding , we can say it as Runtime Errors .
The Concept
The whole idea of having customized Exception Handling is centered around the fact that there needs to be a generic approach of catching and throwing Exceptions.
For implementing custom Exception Handling we need to derive the class CustomException from the system base class ApplicationException. In general, for customizing Exception Handling the following components are necessary:
1. A custom exception class which would host the exception thrown and can be thrown as a new exception.
2. A message class that would host all user - friendly Application messages that need to be displayed.
Creating Custom Exception
VB.NET define your own custom exceptions to identify the occurrence of unexpected events in your code.exceptions are implemented in VB.Net as classes and objects.
-
Create a exception kind of class and inherit it from Exception class.
-
Override the Message property and ToString() method.
For example:
Module Module1
Class NotEnoughBalanceException
Inherits Exception
Public Overrides ReadOnly Property Message() As String
Get
Return "Sorry! Not Engouh Balance"
End Get
End Property
End Class
Class Customer
Private name As String
Private balance As Integer
Public Sub New(ByVal name As String, ByVal opamt As Integer)
Me.name = name
Me.balance = opamt
End Sub
Public Sub Deposit(ByVal amount As Integer)
balance += amount
End Sub
Public Sub Withdraw(ByVal amount As Integer)
If amount > balance Then
Throw New NotEnoughBalanceException()
End If
balance -= amount
End Sub
Public Sub ShowBalance()
Console.WriteLine("Balance of {0} is {1}", name, balance)
End Sub
End Class
Class ExpTest
Public Shared Sub Main()
Dim c As New Customer("Amit", 5000)
Try
c.Deposit(4000)
c.ShowBalance()
c.Withdraw(20000)
c.ShowBalance()
Catch ex As NotEnoughBalanceException
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message)
End Try
End Sub
End Class
End Module
OUTPUT:
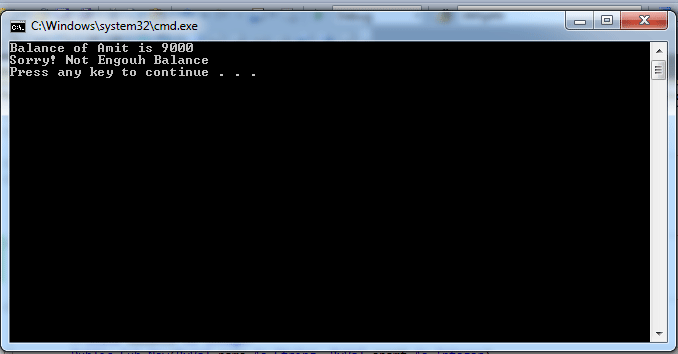
Conclusion:
Hope this article would have helped you in understanding custom exception handling in VB.NET.