Exception Handling in VB.NET
This article will show how to use Exception Handling in VB.NET.
An exception is an error which occurred at run time. there are four keyword which are used to find out error at the run time. In Vb.NET is a special type of class called Exception which are used to pass the message .
Try Statement:
Try statement is a block of statement that are used to trap the error at run time. one try statement can have multiple catch statement.
Syntax:
Try...[catch]...{catch|finally}......End Try
Catch Statement:
Catch statement catch the error from try statement and execute the block of statement.
Syntax:
Catch [<exception>[As<type>]] [when<expression>]
Finally Statement:
Finally statement are used to execute some statement irrespective of error. Finally can only one block at the end.
Example: In this example one try statement has more than one catch statement with the final statement and catch statement catch different type of error from try statement.
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim err As Boolean = True
Dim num As Integer
Try
Console.WriteLine(" please enter number:")
num = Integer.Parse(Console.ReadLine())
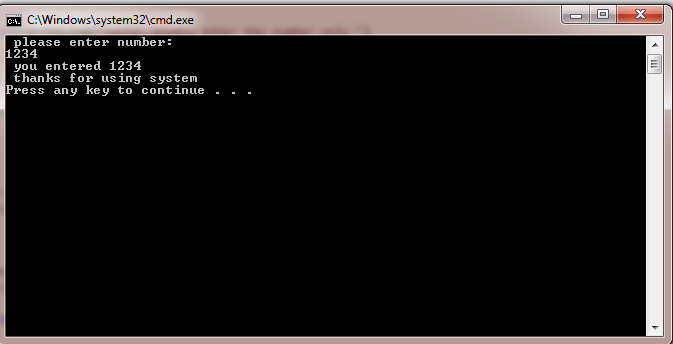
Console.WriteLine(" you entered {0}", num)
err = False
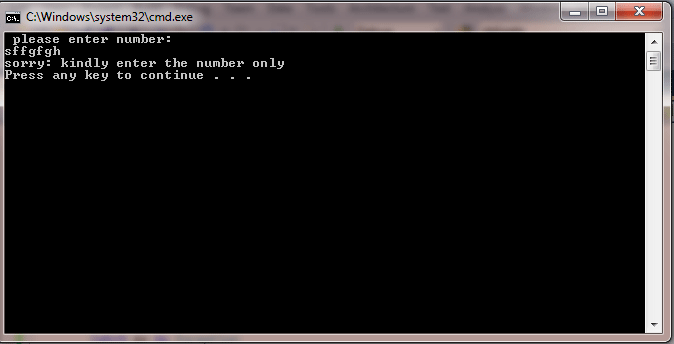
Catch ex As FormatException
Console.WriteLine("sorry: kindly enter the number only ")
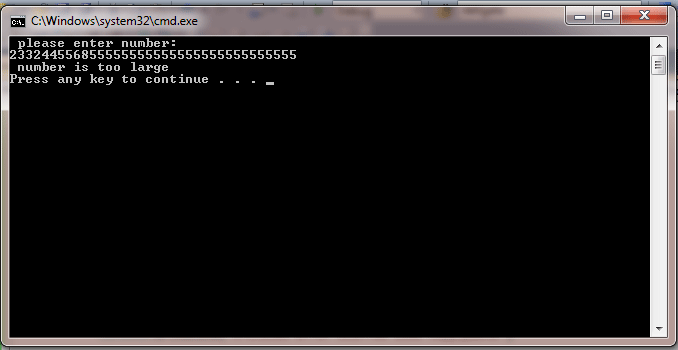
Catch ex As OverflowException
Console.WriteLine(" number is too large")
Catch ex As Exception
Console.WriteLine("critical error occurred like copy, paste")
Finally
If err = False Then
Console.WriteLine(" thanks for using system")
End If
End Try
End Sub
End Module
Output: Enter the number
Output: when we enter the character in place of number it calls the format exception.
Output: When we enter the large number than the range of Integer it calls the overflowexception.