Indexers in VB.NET
In this article I will explain you about indexer in VB.NET.
Indexers, another nifty feature of VB.NET, are similar to the overloaded [] (array subscript) operator in C++. An indexer allows you to access a class instance in terms of a member array.
An indexer declaration may include a set of attributes; a new modifier; a valid combination of the public, private, protected, and internal access modifiers; and one of the virtual, override, or abstract modifiers.
The type of an indexer declaration specifies the element type of the indexer introduced by the declaration. Unless the indexer is an explicit interface member implementation, the type is followed by the keyword this. For an explicit interface member implementation, the type is followed by an interface type, a period (.), and the keyword this. Unlike other members, indexers do not have user defined names.
The formal parameter list of an indexer corresponds to that of a method, with two differences: at least one parameter must be specified, and the ref and out parameter modifiers are not permitted.
The accessors specify the executable statements associated with reading and writing indexer elements.
Even though the syntax for accessing an indexer element is the same as that for an array element, an indexer element is not classified as a variable. Thus, it is not possible to pass an indexer element as a ref or out parameter.
It is an error for an indexer accessor to declare a local variable with the same name as an indexer parameter. With these differences in mind, all rules defined in apply to indexer accessors as well as property accessors.
Indexers and properties, although very similar in concept, differ in the following ways:
-
A property is identified by its name whereas an indexer is identified by its signature.
-
A property is accessed through a simple-name or a member-access whereas an indexer element is accessed through an element-access.
-
A property can be a static member whereas an indexer is always an instance member.
-
A get accessor of a property corresponds to a method with no parameters whereas a get accessor of an indexer corresponds to a method with the same formal parameter list as the indexer.
-
A set accessor of a property corresponds to a method with a single parameter named value whereas a set accessor of an indexer corresponds to a method with the same formal parameter list as the indexer, plus an additional parameter named value.
To understand these concepts, refer to the code in Listing 5.56.
Listing 5.56: Indexer Example
Imports System
Imports System.Net
Class GetDNSaliases
Private m_arrAlias As String()
Public Sub Fetch(ByVal strHost As String)
Dim iphe As IPHostEntry = Dns.GetHostByAddress(strHost)
m_arrAlias = iphe.Aliases
End Sub
Default Public ReadOnly Property Item(ByVal nIndex As Integer) As String
'indexer
Get
Return m_arrAlias(nIndex)
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Count() As Integer
' property
Get
Return m_arrAlias.GetUpperBound(0)
End Get
End Property
End Class
Class MyApp
Public Shared str1 As String
Public Shared Sub Main()
Dim myGetDNSaliases As New GetDNSaliases()
Do
Try
Console.WriteLine("write a valid IP Address and press ENTER (to exit enter ""q"").")
If (str1 = Console.ReadLine()) = "q" Then
Exit Try
End If
myGetDNSaliases.Fetch(str1)
Dim nCount As Int32 = myGetDNSaliases.Count
Console.WriteLine("Found {1} aliases for IP {0}", str1, nCount)
Dim i As Int32 = 0
While i < nCount
Console.WriteLine(myGetDNSaliases(i))
System.Math.Max(System.Threading.Interlocked.Increment(i), i - 1)
End While
Catch e As Exception
Console.WriteLine("Exception occurred!{0}" & vbCr & vbLf, e.ToString())
Finally
'final code to be executed
End Try
Loop While True
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Class
The code in this listing generates the display in Figure 5.16.
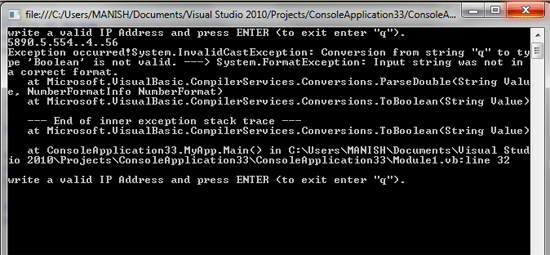
Conclusion
Hope this article would have helped you in understanding indexer in VB.NET.