Definition
Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET or VB .NET) is a version of Microsoft's Visual Basic that was designed, as part of the company's .NET product group, to make Web services applications easier to develop. According to Microsoft, VB .NET was reengineered, rather than released as VB 6.0 with added features, to facilitate making fundamental changes to the language. VB.NET is the first fully object-oriented programming (OOP) version of Visual Basic, and as such, supports OOP concepts such as abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism, and aggregation.
Note : I am using Visual Studio 2008 in all my articles.
Revision of "Hello World"
Listing 5.1 provides another quick look at the classic "Hello World" application.
Listing 5.1: HelloWorld.vb, Hello World Example
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Console.WriteLine("Hello, World")
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue")
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module
You can copy the code in Listing 5.1 into any editor such as Notepad and save the file as HelloWorld.vb. To compile the program, type the following at the command line:
csc IntroductionVB.vb
Then run the program by typing HelloWorld at command line. The program output is shown in Figure 5.1.
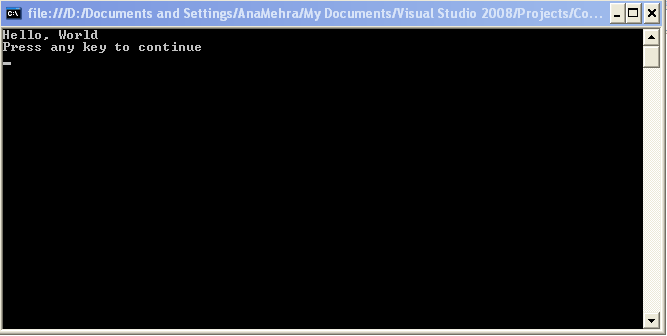
Figure 5.1: Hello World Example Output
As discussed in Chapters 3 and 4, using the System statement makes the system namespace and its classes available in the program. The class statement followed by the name of the class defines a new class. Every program should have at least one Main method, which is the entry point of the application.
The System.Console class defines functionality to read from and write to the system console. The Console.WriteLine method writes a string to the console.
Object Class and Types
In .NET, the Object class is the root of all types. All types are implicitly derived from this class so they have access to the methods defined in the Object class. These methods are described in the Table 5.1.
|
Method
|
Description
|
|
Equals
|
Compares whether two object instances are equal. Returns true if two objects are equal; otherwise, returns false.
|
|
ReferenceEquals
|
Compares two object instances. Returns true if both are same instances; otherwise, returns false.
|
|
GetHashCode
|
Returns a hash code for the object.
|
|
GetType
|
Returns a Type object, which holds the types of current instance.
|
|
ToString
|
Converts an instance to a string type and returns a String object.
|
Table 5.1: The Object Class Methods and Their Descriptions
Type Information
The GetType method of the Object class returns a Type object. The Type class is useful when you need to know the internal details of a class such as the type of the class, its attributes, methods, properties, globally unique identifier, name, and fullname. Listing 5.2 demonstrates use of the GetType method.
Listing 5.2: Type Information Example
Dim cls1 As New AClass()
Dim cls2 As New BClass()
Dim type1 As Type = cls1.[GetType]()
Dim type2 As Type = cls2.[GetType]()
Console.WriteLine(type1.BaseType)
Console.WriteLine(type1.Name)
Console.WriteLine(type1.FullName)
Console.WriteLine(type1.[Namespace])
You can use many other methods (GetFields, GetEvents, GetInterfaces, etc.) and properties to obtain more information about an object.
Comparing Two Objects
The Object class's Equals and ReferenceEquals methods can be used to compare two objects and their instances, respectively. Listing 5.3 shows one such use of the Equals method.
Listing 5.3: Compare.cs, Compare Two Objects Example
Module Module1
' Define A Class
Public Class AClass
Inherits [Object]
Private Sub AMethod()
Console.WriteLine("A method")
End Sub
End Class
' Define B Class
Public Class BClass
Inherits AClass
Private Sub BMethod()
Console.WriteLine("B method")
End Sub
End Class
Sub Main()
Dim cls1 As New AClass()
Dim cls2 As New BClass()
Dim str1 As String = "Test"
Dim str2 As String = "Test"
Console.WriteLine([Object].Equals(cls1, cls2))
Console.WriteLine([Object].Equals(str1, str2))
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to continue")
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module
Figure 5.2 shows the result of the program in Listing 5.3.
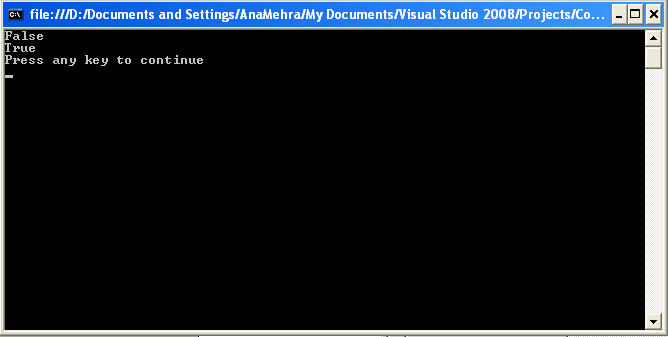
Figure 5.2: Screen Generated by Listing 5.3.
You use ReferenceEquals in the same manner, as shown:
Console.WriteLine([Object].ReferenceEquals(obj1, obj2))
Convert to a String Type
The ToString method of the Object class converts a type to a string type. Because converting to a string type is a very common programming practice, Microsoft defined the ToString method in the Object class, thus making it available to each type in the .NET world through inheritance. The example code in Listing 5.4 converts an integer type and a floating-point number type to a string type.
Listing 5.4: ToString.cs, Convert to String Example
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim i As Integer = 12
Dim flt As Single = 12.005F
Console.WriteLine(i.ToString())
Console.WriteLine(flt.ToString())
End Sub
End Module
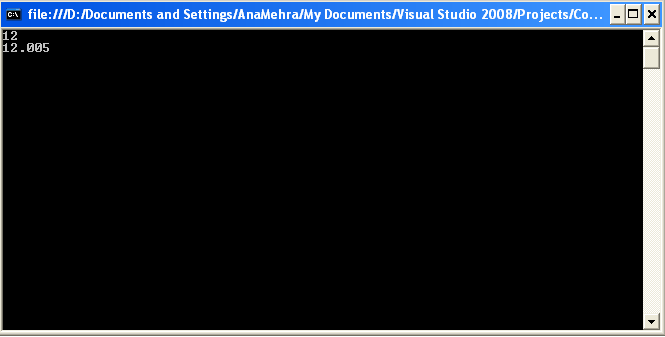
Figure 5.3: Screen Generated by Listing 5.4.
Hash Code
You don't use a hash code in regular programming practices, but it's useful if you want to use a type in hashing algorithms such as a hash table. A hash table provides a quick lookup, much like a dictionary. Each member of the hash table has a key value and the object can be referenced by using the key. All members of a class have a memory area defined in the hash table of that class. Members with different names can have the same values but different hash code. By using the method GetHashCode, .NET gives you the flexibility to access the hash code of an object directly and work with it. A derived class can override this method. It's not necessary to return the same hash code for two objects referencing the same value.
Conclusion
See other articles on the website on .NET and VB.NET.