Throwing an Exception in C#
In this article we will explain how to throw the Exception in a program.
Exception handling is very common in programs. Exceptions are used to indicate that an error has occurred while running the program. All the exceptions in the .NET Framework are derived from the System.Exception class. The error is handled through the process of exception handling. Exception objects are used to describe that errors are occurred and then thrown with the throw keyword. Throw is a reserved keyword in c#.
The exception object has some important properties. Some of them are given below
| Property |
Description |
| Message |
Gives detailed information about the message. |
| StackTrace |
Gives the function stack to show where exception is thrown. |
| Targetsite |
Shows which method throws the exception. |
Syntax
Catch(Exception e)
{
...
Throw e
}
Example
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
public class ThrowExample
{
public static void Ma(Int32 marks)
{
if (marks < 0)
{
// throw an argument out of range exception if the marks is less than zero.
throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("marks Cannot Be Negative ");
}
}
public static void Main()
{
try
{
Ma(-2);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(String.Concat(e.StackTrace, e.Message));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
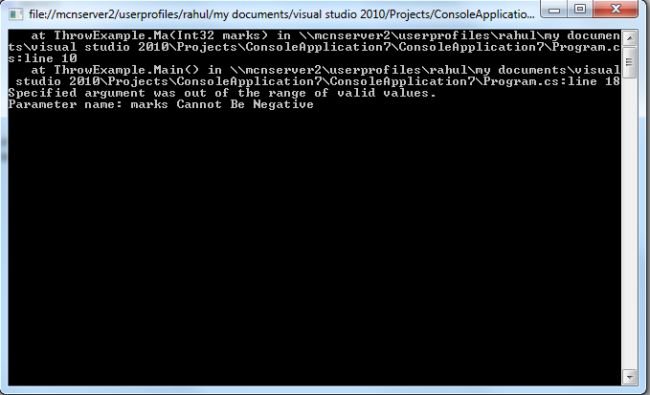
In this example we have a function called Ma, which takes marks as an argument. In this function we check if the marks are negative value, and if so, throw ArgumentOutOfRangeException.
The output of following program