IndexOutofRangeException in .Net
In this article we will explain how we can handle the IndexOutofRangeException in DotNet.
Exception handling is very common in programs. Exceptions are used to indicate that an error has occurred while running the program. IndexOutofRangeException will typically occur when an attempt is made to access an element at an index greater than the maximum allowable index. Computers can't handle this situation without using exception handling so its gives an error or Exception. This exception is called IndexOutofRangeException.
Example
Consider the following program
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] numbers = new int[2];
numbers[0] = 11;
numbers[1] = 21;
numbers[2] = 24;
foreach (int i in numbers)
Console.WriteLine(i);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
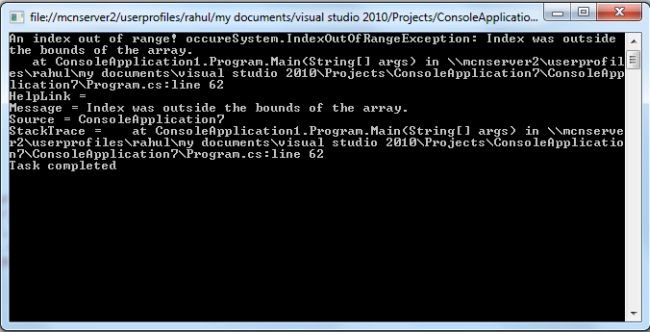
The following image show the exception in the Program
The following example handle the exception in the program
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] numbers = new int[2];
try
{
numbers[0] = 11;
numbers[1] = 21;
numbers[2] = 24;
foreach (int i in numbers)
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("An index out of range! occure" + ex);
Console.WriteLine("HelpLink = {0}", ex.HelpLink);
Console.WriteLine("Message = {0}", ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Source = {0}", ex.Source);
Console.WriteLine("StackTrace = {0}", ex.StackTrace);
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("Task completed");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
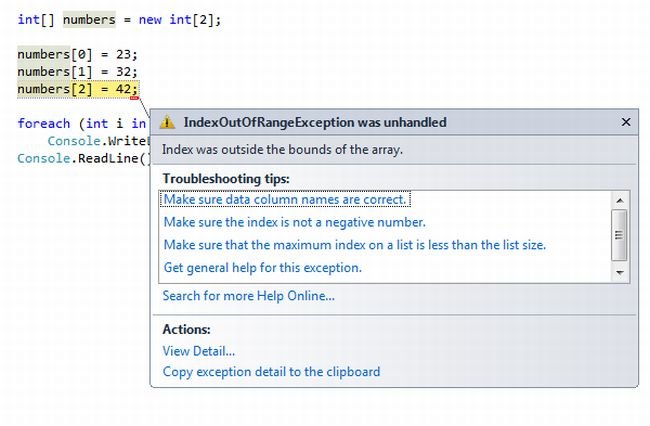
The output of following program is