LINQ to SQL in VB.NET
This article defines how to use LINQ query with SQL.
Linq to SQL
LINQ to SQL fully supports transactions, views, and stored procedures. It also provides an easy way to integrate data validation and business logic rules into your data model. This example defines the basic idea of LINQ to SQL Query using code.
Step 1
Open visual studio 2010 and create a new project -> Web -> ASP.NET Web Application.
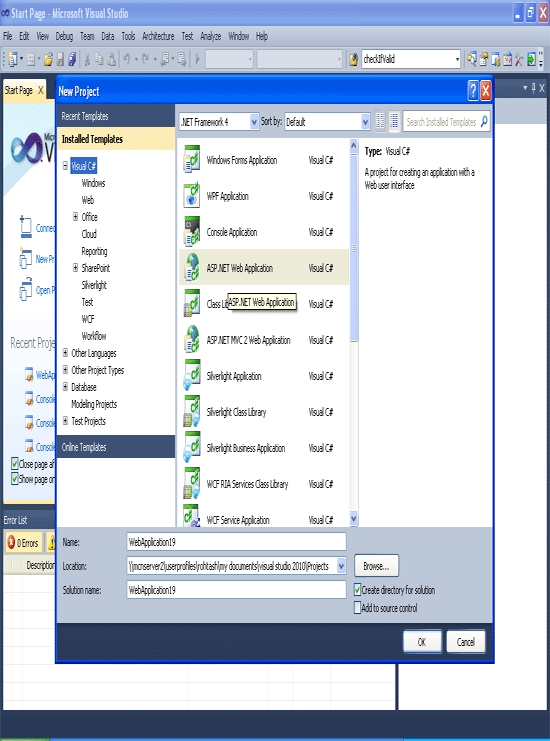
Step 2
Once project is load we need to create a database. Right Click the App_data -> Add -> New Item.
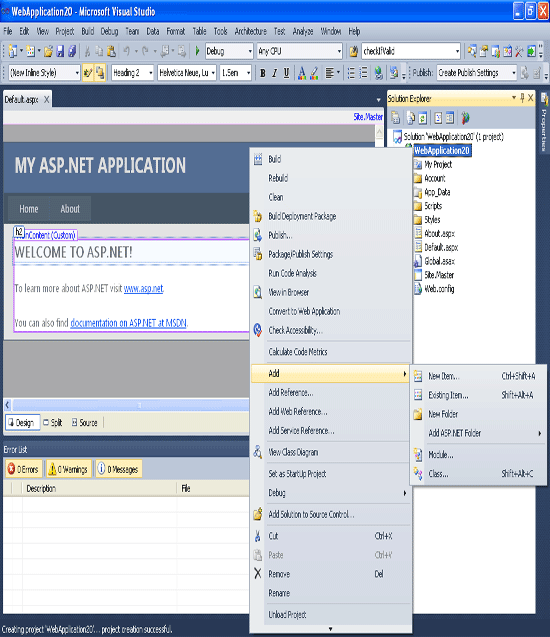
Step 3
Now select SQL server Database.
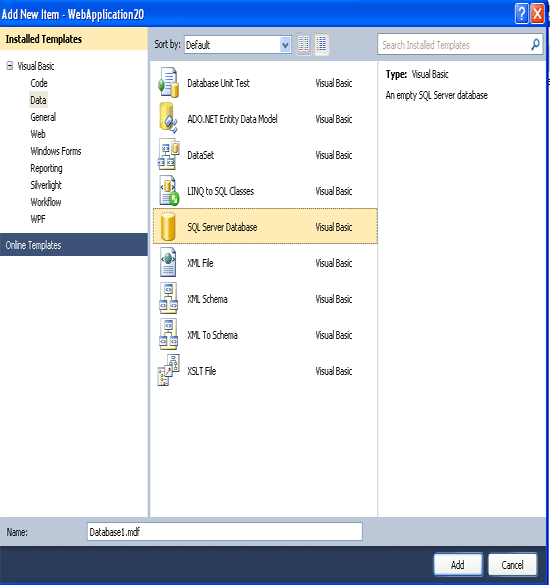
Step 4
Now change the name mcndesktop01 database and create a new table with the login name which has the two field username and password.
Now open the server explorer from menu item view. view->server Explorer.
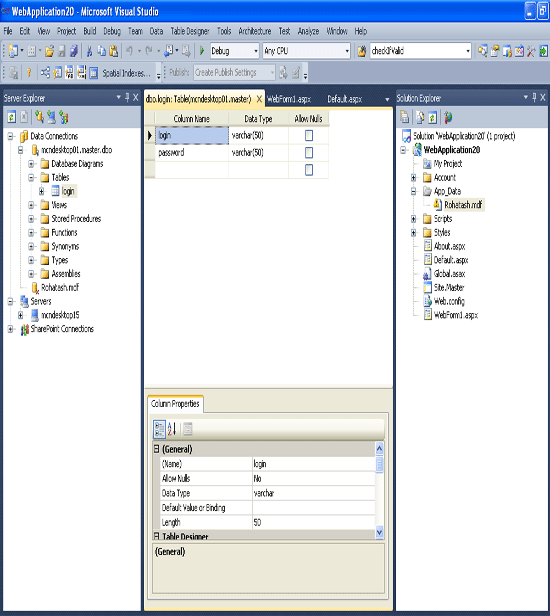
Step 5
Insert the data into login table.
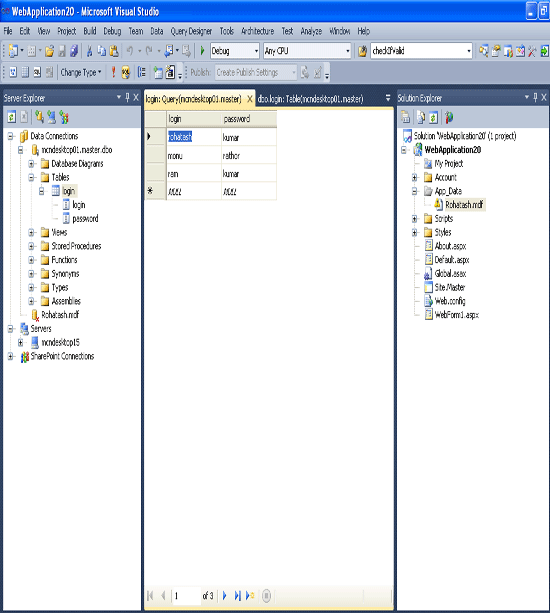
Step 6
Now we can add a LINQ to SQL Class
Right click on "LinqBasic" Application > Add > New Item
Select "LINQ to SQL Classes" Name as "Linq.dbml" and click add.
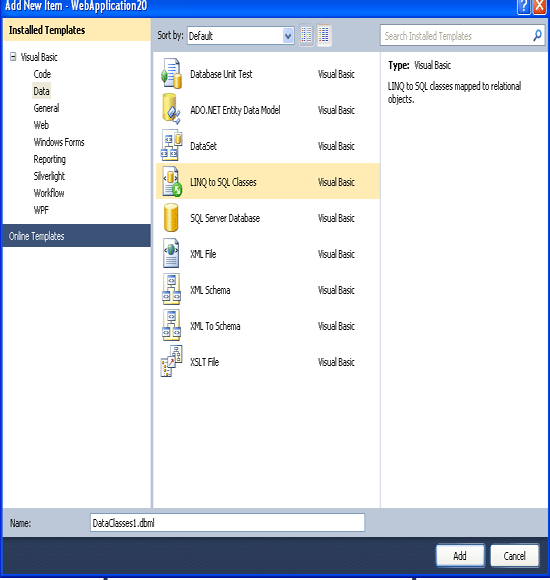
Step 7
Now you will get "Object Relational Designer " window. Drag and drop the login table from "server explorer" to "Object Relational Designer". It will appear as follows.
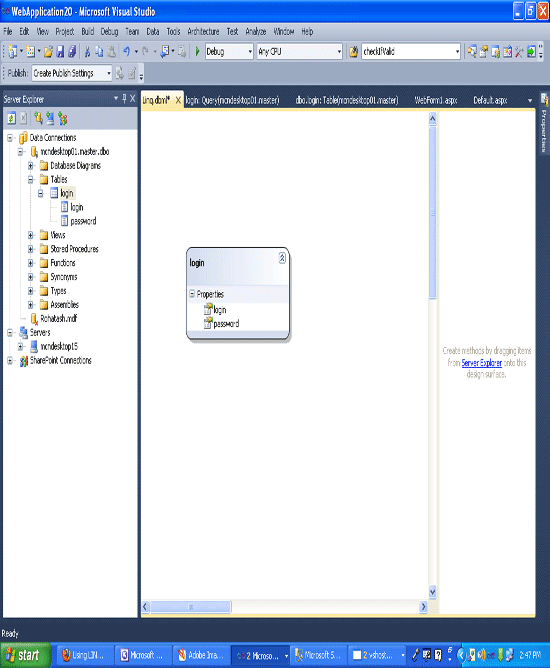
Save all and build. Switch to design view. Drag and drop the "GridView" from Toolbox to designer view.
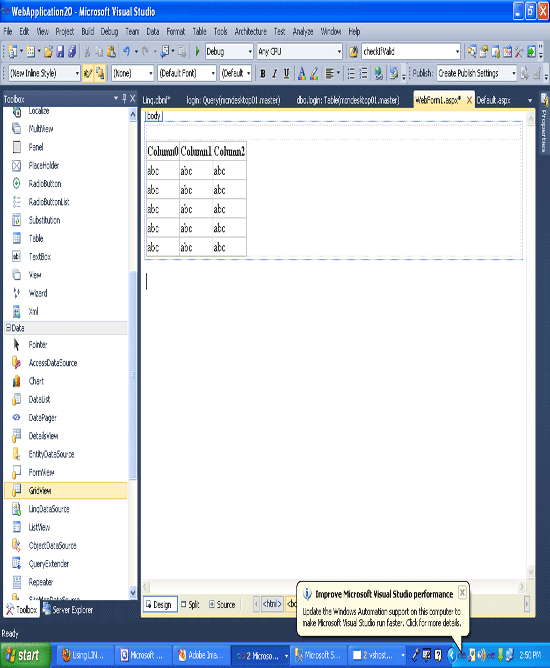
Step 8
Now Double click on the form and add the following code with form load.
C# code
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DataClasses1DataContext bt = new DataClasses1DataContext();
var m = from em in bt.logins select em;
GridView1.DataSource =m;
GridView1.DataBind();
}
VB code
using convertor tool (c# to VB)
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object,ByVal e As System.EventArgs)Handles Me.Load
Dim bt As New DataClass1DataContext()
Dim m = From em In bt.logins Select em
GridView1.DataSource = m
GridView1.DataBind()
End Sub
Step 9
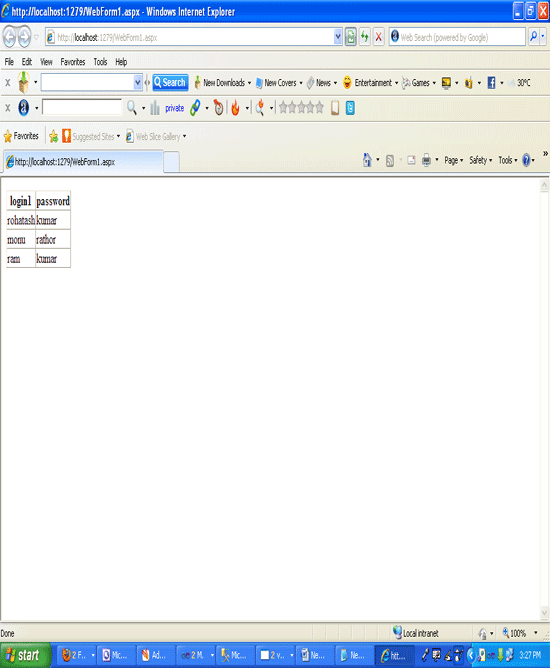
Now run the application.
Understanding the DataContext Class